Eating clementines has the following advantages for your health and well-being:

- Packed with Vitamin C
Vitamin C, which is necessary for a strong immune system, is abundant in clementines. You can get a good amount of this potent antioxidant in a single clementine, which is the recommended daily intake. Vitamin C strengthens the body’s defenses against infections and diseases, promotes wound healing, and shields cells from harm.
- Helps Maintain Healthy Skin
Clementines’ high vitamin C content encourages the formation of collagen, which is necessary for the elasticity and repair of skin. By lessening the appearance of wrinkles and enhancing general skin health, regular clementine consumption can help maintain firm, smooth, and youthful skin. Additionally, the antioxidants shield your skin from UV radiation and other environmental harm.
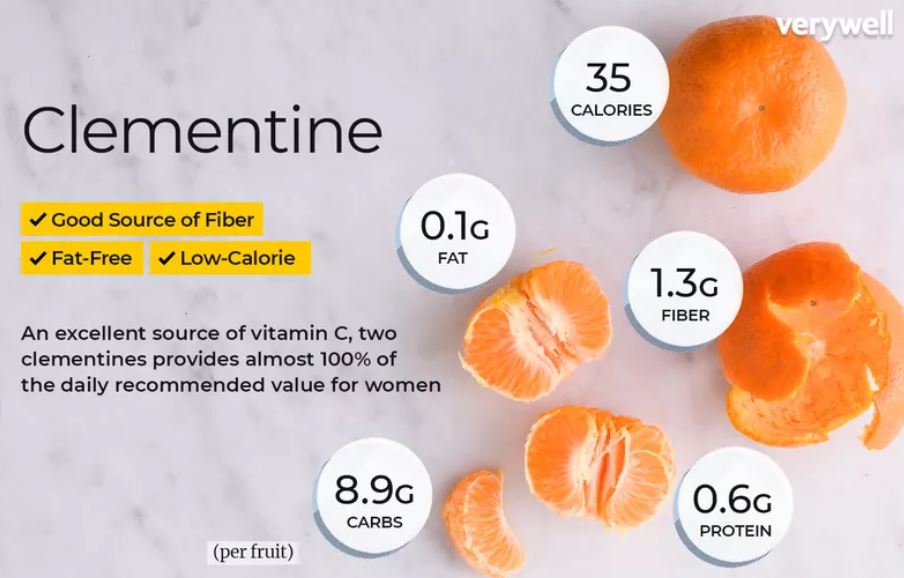
- Minimum Calorie Content
Clementines are a great snack for people watching their weight because they are naturally low in calories. They can satiate your sweet tooth without adding extra calories, as each fruit has only about 35 calories. Additionally, they contain a lot of water, which keeps you hydrated and full.
- A Good Fiber Source
Dietary fiber, found in clementines, fosters gut health and facilitates digestion. Consuming fruits high in fiber, such as clementines, promotes a healthy digestive system, prevents constipation, and helps control bowel movements. Additionally, by reducing cholesterol, fiber can support heart health and aid in blood sugar regulation.
- Encourages Hydration
The high water content of clementines aids in hydration. Maintaining proper hydration is critical for general health, impacting everything from digestion and skin health to energy levels. Clementines are a delicious way to boost your daily water intake, particularly after working out or in hot weather.
- Packed with Antioxidants
Flavonoids and carotenoids are two of the many antioxidants found in clementines. By aiding in the body’s defense against dangerous free radicals, these substances lessen oxidative stress and the chance of developing chronic illnesses like cancer and heart disease. Additionally, antioxidants help keep cells healthy and delay the onset of aging.
- Encourages the Health of the Heart
Clementines contain potassium, which is good for the heart. By negating the effects of sodium, potassium lowers the risk of hypertension and aids in blood pressure regulation. Furthermore, clementines’ fiber and antioxidants lower inflammation and support healthy cholesterol levels, both of which are critical for cardiovascular health.
- Convenient and Kid-Friendly
Because they are small, seedless, and simple to peel, clementines are a great kid-friendly snack. Kids love them because of their naturally sweet flavor, which makes them a healthy substitute for processed snacks. They are also very convenient for people of all ages to snack on while they are on the go.
- Enhances Eye Well-being
The body transforms beta-carotene and other carotenoids found in clementines into vitamin A. In order to prevent diseases like night blindness and age-related macular degeneration, vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy eyesight.
Including clementines in your diet is a tasty and simple way to increase your intake of nutrients and promote your general health.

